Blockchain sidechain technology is vital for increasing blockchain scalability and interoperability. This guide explains how the technology works with examples.
Top blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum have historically suffered from a lack of scalability. There are so many platforms with almost innumerable use cases, but sending crypto assets on-chain often forces users to choose between time and costs. Fortunately, there is a scalability solution in development called a blockchain sidechain. Now let's looks at the side chain definition and the importance of this technology.
What Is a Sidechain?
A sidechain consists of a blockchain network tied to the main chain via a two-way peg. Let’s use Bitcoin as an example.
If one wants to utilize a sidechain connected to the Bitcoin protocol, they must lock up a certain amount of BTC by sending it to an output address on the sidechain. After a short time, the sent funds are now available on the sidechain.
Sidechains are not to be confused with blockchain forks, which occur when a group of users on the network decides to split into a new blockchain altogether. In the case of blockchain hard forks, the goal is to create an entirely new mainchain that has complete autonomy. The BCH blockchain is the most prominent example of a Bitcoin fork. In contrast, sidechains aim to work alongside the mainchain to achieve a high level of interoperability.
The Importance of A Blockchain Sidechain
Developers and blockchain participants use sidechains to test features and experience other use cases not normally available on the network main chain. Sidechains can also be used to speed up transaction finality and lower overall transaction costs.
Sidechains are vital for blockchain accessibility, as they enable users to harness their held crypto assets for various use cases. For example, in the case of Bitcoin transactions, there’s no need to spend a ton on fees or wait potentially hours for the transaction to validate.
Sidechain Security
Sidechain security varies based on the network. In most cases, a sidechain utilizes its own form of security through a consensus method like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). That said, sidechains need various dedicated members to keep their security strong. Otherwise, they’ll fall victim to hacks and other threats.
In some special cases, like with Ardor, sidechains inherit the security of the main chain. All transactions are checked and validated via the main chain, with the sidechain acting more as an improved way to interact with certain protocols.
Sidechain Blockchain Platforms
Today many projects are working on sidechain technology. Let's take a look at a few popular examples and dive into how they work.
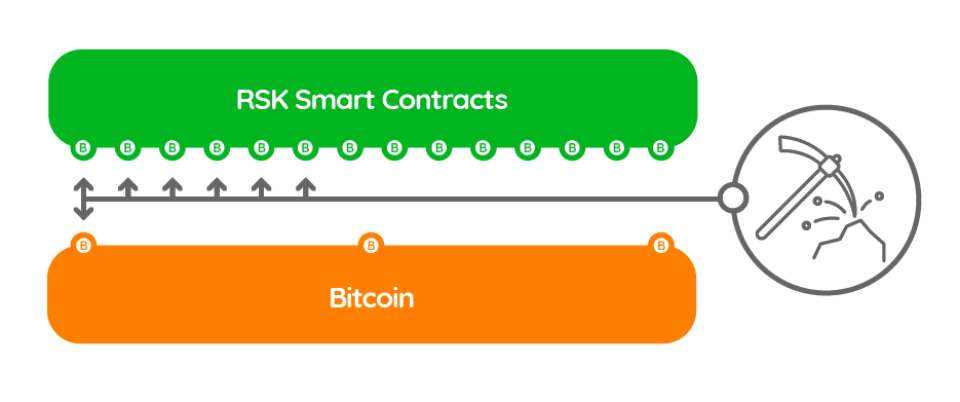
RSK (RootStock)
Reason of Creation
RootStock is pegged to the Bitcoin blockchain and features decentralized applications for users to interact with. When locking up their Bitcoin (BTC), assets are turned into Smart Bitcoin (SBTC), which holders can utilize with the network’s smart contracts. As you may learn in a blockchain developer course, smart contracts are a popular technology used on many blockchain networks, especially for Ethereum programming.
For example, if a worker and a client work together using Ethereum, they’ll want to establish a smart contract. The client would lock up whatever payment is agreed upon in a smart contract. From there, they’ll fill out the requirements for the payment to release, along with a set timeframe to do so. A worker then fulfills those requirements, submits their work, and the payment is automatically released.
Smart contracts enable decentralized applications on the Ethereum network, but the code for such agreements isn’t natively integrated on the Bitcoin mainchain. RootStock's Bitcoin sidechain enables the use of smart contracts via a sidechain, meaning users don’t have to convert Bitcoin to other assets to make use of this same functionality. RSK smart contracts are automated, secure if-then statements used to create a trustless environment for two parties to transact value.
Sidechain Details
More specifically, RootStock enables users to lend and borrow their Bitcoin. Lenders can earn interest on their lent Bitcoin, and borrowers have a fair amount of control over their interest payments.
In this case, RootStock removes the need for a traditional bank or other third-party financial institution. Typically, a bank has the final say in a lending and borrowing agreement, taking fees and facilitating a deal it doesn’t necessarily need to have a place in. With RSK, the two participating parties can decide contract terms and have them enforced by a smart contract instead.
RIFOS
Eventually, RootStock will expand its infrastructure via RIFOS, a multi-faceted platform for users to manage their identity, communications, file storage, and more, all in one decentralized space. RIFOS, combined with smart contract technology, supports blockchain-based decentralized internet usage.
Ardor’s Blockchain
Reason of Creation
Ardor’s blockchain network utilizes a parent-to-child chain architecture. In this case, the parent blockchain is Ardor’s mainchain that stores all transactions, provides all security protocols, and more. Blockchain developers can create unique child chains tied to the main chain.
Each child chain has its own cryptocurrency and use case, and those cryptocurrencies are all listed on a singular Ardor-centric exchange for trading. Basically, Ardor is creating its own network of blockchain economies that are all interoperable with one another. The idea is to use a child chain as a database, or another sort of record-keeping, for whatever the developer intends. Ardor streamlines the blockchain creation process by keeping security and transaction validation on the mainchain to avoid clogging up a child chain.
Features
Ardor is entirely Proof of Stake, making it so anyone can participate in network security and governance without needing expensive hardware. In addition, the network’s child chain technology makes it so anyone can utilize their own blockchain without understanding code or development, streamlining blockchain accessibility for users worldwide.
Token
Ardor’s ARDR token is used for governance, while child chains each have their own cryptocurrencies for interaction.
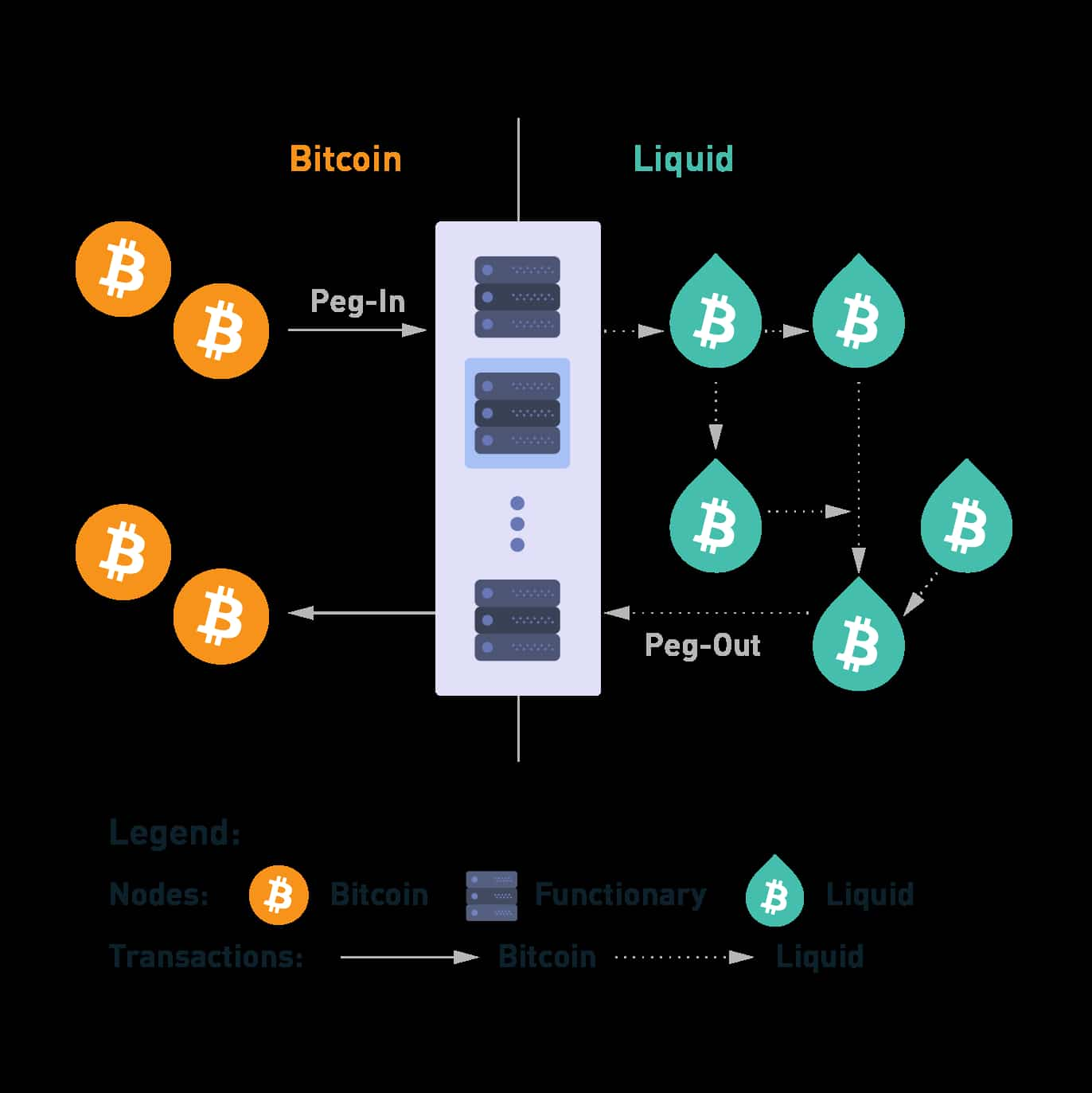
Liquid
Reason of Creation
Liquid is a network for decentralized applications such as lending platforms and exchanges. The project’s currency, LBTC, is backed 1:1 by Bitcoin.
Users can convert their BTC to LBTC and use it to acquire other Liquid-based cryptocurrencies, lend it out for interest, or even issue new stablecoins and other types of assets. Similar to RootStock, Liquid provides Bitcoin holders with additional use cases not available on the Bitcoin mainchain.
Liquid’s Federation
Liquid stands out due to its governance model, or federation. The Liquid Federation is made up of three tiers - functionaries, members, and full nodes.
- Functionaries are specialized users that validate transactions between Bitcoin and the Liquid Network.
- Members hold LBTC to vote on network proposals.
- Full Nodes double-check Functionaries' activity to make sure transactions are validating correctly.
While the first two tiers are vital for Liquid’s functionality, Full Nodes are the last straw. Full Nodes are the most dedicated Liquid users, ensuring transactions can always be verified and that no bad actors are messing with the network.
Conclusion
Sidechain blockchain networks have a long way to go, but they’re a solid foundation aiming to solve interoperability, scalability, and the bottleneck of high transaction fees. Many of these projects enable Bitcoin holders to enjoy additional use cases without converting to other cryptocurrencies like Ethereum. With the right combination of sidechains, it's possible that one day a single blockchain network can serve all of a user’s needs.
📧Komodo Newsletter
If you'd like to learn more about blockchain technology and keep up with Komodo's progress, subscribe to our newsletter. Begin your blockchain journey with Komodo today.

