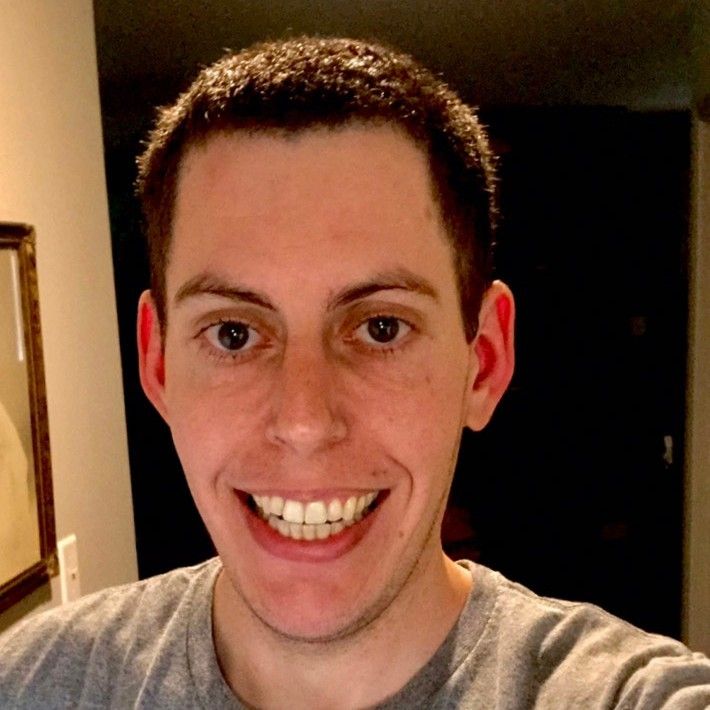
Most crypto traders that have interacted with decentralized exchanges are familiar with automated market making protocols like Uniswap and SushiSwap. However, there are actually a few other types of DEX liquidity models that exist. Here's how they compare.
What Is a Market Maker?
Any exchange, whether it is decentralized like the examples listed here or centralized, relies upon market makers. In its simplest form, a market maker is someone (a real human or an automated bot) that puts up orders on a trading platform. This creates liquidity on the platform, enabling market takers to have the ability to accept the trade. If you're interested in learning more about how today's most popular trading platforms work, check out our list of decentralized exchanges.
Now let's look at how the above market maker example is applied in practice on DEXs that use automated market makers (AMMs) and peer-to-peer order books.
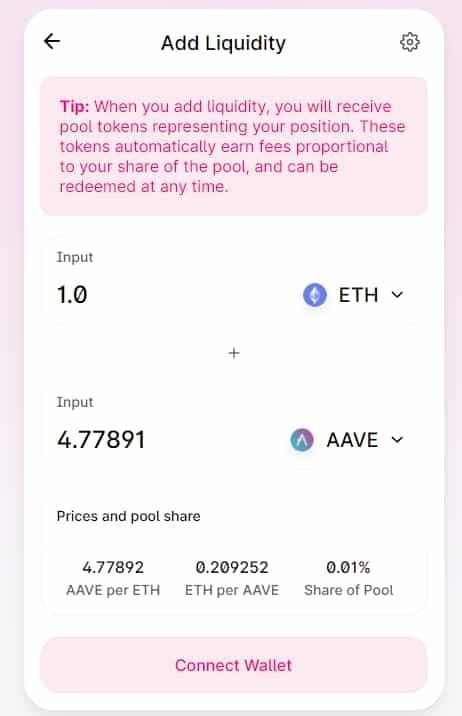
What Are Automated Market Makers (AMMs)?
The Uniswap exchange and SushiSwap exchange are two of the most popular DEXs around today. Likewise, UNI and SUSHI are two of the top AMM coins by market cap.
With their liquidity solutions, smart contracts actually take over the process of the trade. Trades are conducted within AMM crypto liquidity pools rather than between users. Each trading pair has its own pool. The pool continuously reorganizes by a ratio as users buy and sell. Liquidity pools incentivize liquidity providers to supply assets. This is what is known as automated market making.
Uniswap has trading pairs with a liquidity pool ratio of 50/50 between Ethereum (ETH) and any given ERC-20 token. Balancer - another popular ERC-20 DEX - improves upon the AMM model by allowing users to create dynamic liquidity pools of up to eight different assets at any ratio. Prices of assets on Balancer are also determined by liquidity pool ratios. The 1inch DEX aggregator is another popular option for users who want to find optimal prices of assets across major decentralized exchanges as well as decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms.
What Are Off-Chain Order Books?
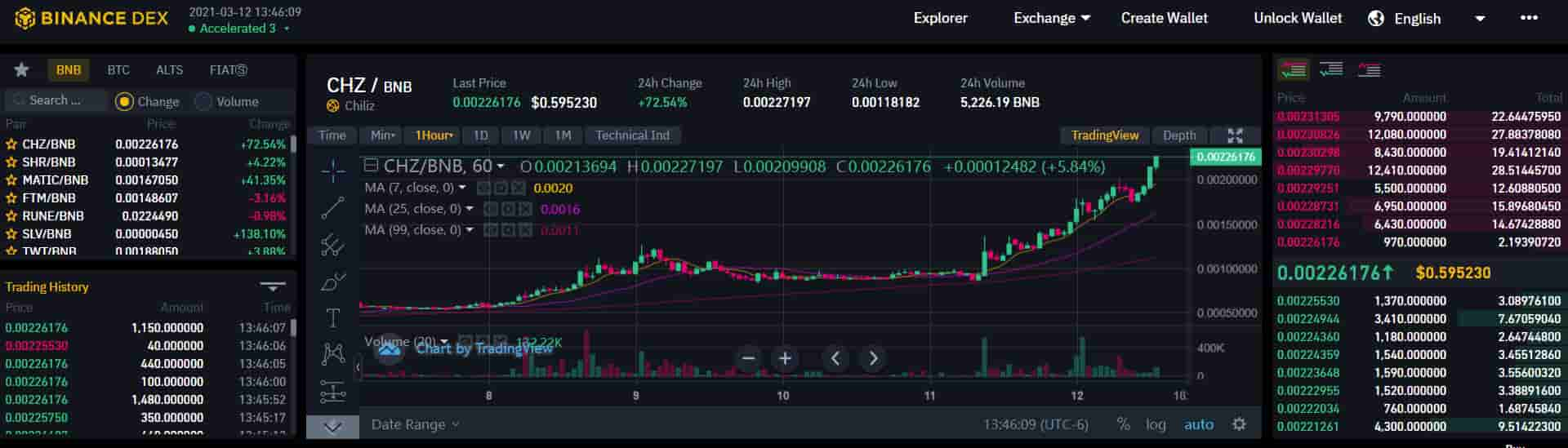
Binance DEX, IDEX, and EtherDelta are a few examples of DEXs that implement off-chain order books.
The individual user inputs a specific price and a volume for an order. The users collectively determine the price - not the exchange. Off-chain order books bring a degree of centralization to DEXs. For example, one entity could control the entire order book. Malicious actors could front run or misrepresent orders.
The benefit of off-chain order books is speed and cost efficiency. While not as fast as a centralized exchange since orders must be settled on-chain, off-chain order books are more secure since the DEXs themselves are non-custodial - meaning the user is in control of their own private keys, thus having control over their own funds.
What Are On-Chain Order Books?
Decentralized exchanges like StellarTerm and Bitshares run 100% on-chain. However, this model isn't a popular option because it has proven to be inefficient due to limitations in throughput for most blockchains.
Writing every order on-chain adds transparency since the trader doesn't have to trust an intermediary to relay the orders. However, users have to pay a fee for each node on the network to record the order. Furthermore, the trader needs to wait until a miner (Proof of Work consensus) or validator (Proof of Stake or Delegated Proof of Stake consensus) adds their transaction to the blockchain.
On-chain order books also make it easier for bad actors to front run, which means a validator or miner can see the trader's order before it's confirmed on the blockchain and add their own order first.
Komodo Wallet — Implementing A Hybrid Liquidity Solution
Komodo Wallet offers a hybrid solution that fits somewhere in between on-chain and off-chain. The order books are off-chain but decentralized, mitigating any risks of malicious actors controlling them. Order matching takes place on-chain, and trades take place on a peer-to-peer network.
With Komodo Wallet, users make orders from mobile, desktop, or command line interfaces. Liquidity providers on Komodo's DEX network leverage a shared liquidity pool. With Komodo's open-source technology, anyone can launch their own branded DEX and use shared liquidity.
Unlike most decentralized exchanges, Komodo Wallet doesn't limit trading to a single blockchain network. Komodo Wallet is chain agnostic - supporting Bitcoin, Litecoin, Ethereum, Komodo, and dozens of additional networks thanks to atomic swap technology and is even flexible enough to add new liquidity models like AMMs and bridges to other DEXs.

